Difference between revisions of "OpenLayers Tutorial Pt"
| Line 208: | Line 208: | ||
* [http://www.json.org/ Introduction to JSON] | * [http://www.json.org/ Introduction to JSON] | ||
* [http://getfirebug.com/logging.html Debugging with Firebug] | * [http://getfirebug.com/logging.html Debugging with Firebug] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Obter o Código == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Getting the Code | ||
| + | |||
| + | Releases are made available on the downloads page. Additionally, if you wish to use OpenLayers in a web application, you can include http://www.openlayers.org/api/OpenLayers.js in your page, to always get the latest release. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The code is also available in our Subversion repository. Using Subversion, you can keep up to the absolute bleeding edge of the code. If you wish to report a bug in the API, and you are able to use Subversion, please see if the bug has been fixed in Subversion first: OpenLayers is under rapid development, so things change quickly. | ||
| + | |||
| + | If you don't have Subversion or don't want to download the code, you can still try some live examples on openlayers.org. If you're familiar with JavaScript, try viewing the source of the examples to get an idea how the OpenLayers library is used. | ||
| + | |||
| + | OpenLayers is still undergoing rapid development, so expect a lot to change in the next few weeks and months. We need your support! Please check the wiki for the very latest updates and documentation, and thank you for taking an interest. | ||
Revision as of 08:44, 28 September 2008
Introdução
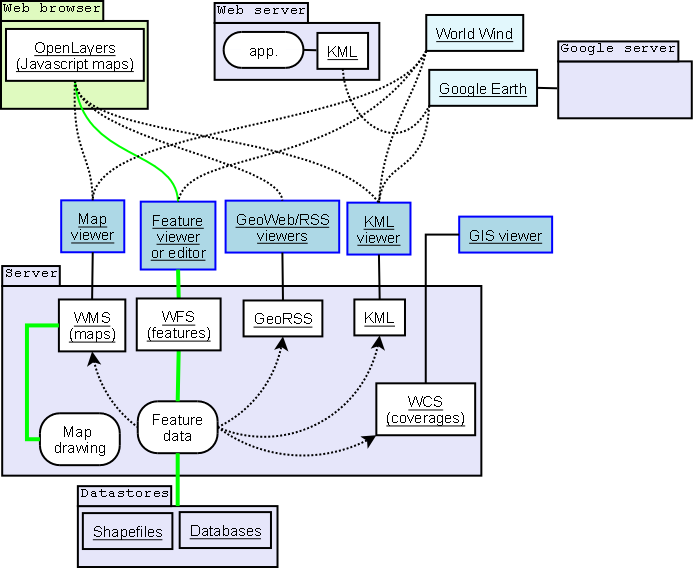
OpenLayers é uma biblioteca JavaScript open-source, sob licença BSD, que permite construir páginas web contendo informação geo-espacial dinâmica e independente de servidor. Implementa uma API JavaSript, ainda em desenvolvimento, que permite a construção de aplicações geográficas web-based, disponilbilizando APIs como o Google Maps e o MSN Virtual Earth, desta feita, como software livre. Criado pela MetaCarta, que continua a desempenhar um papel activo no suporte e gestão deste projecto, pertence desde de Novembro de 2007 à Open Source Geospatial Foundation que apoia e promove o desenvolvimento cooperativo de tecnologias e dados geo-espaciais.
"Olá Mundo" OpenLayers
Map e Layer são dois conceitos importantes na construção de um mapa com o API OpenLayers. Um Map guarda informação acerca do mapa: projecção base, extensão, unidades, etc.
Dentro do Map a informação é disponibilizada via Layer's, que sendo a fonte de informação, define como esta deve ser requerida e apresentada.
O OpenLayers suporta a inserção de mapas em quase todas as tags html de tipo block-level, (como por exemplo TODO)
Para construir um visualizador OpenLayers numa página web, basta inseri-lo numa tag deste tipo
incluindo uma tag script para incluir a biblioteca OpenLayers no código da página html.
<html>
<head>
<title>OpenLayers Example</title>
<script src="http://openlayers.org/api/OpenLayers.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div style="width:100%; height:100%" id="map"></div>
Cria-se o Map através do construtor OpenLaer.Map, que tem como o argumento o elemento HTML onde estará contido ou o seu ID
var map = new OpenLayers.Map('map');
O OpenLayers suporta vários data sources, WMS, Yahoo! Maps, WorldWind e etc.
Neste exemplo utiliza-se como Map um WMS da MetaCarta.
Para adicionar uma Layer ao Map, o construtor do Layer tem como parametros a URL do WMS server usado, e um objecto que contem os parametros a serem anexados ao pedido WMS.
var wms = new OpenLayers.Layer.WMS(
"http://labs.metacarta.com/wms/vmap0",
{'layers':'basic'} );
map.addLayer(wms);
Para apresentar o mapa é preciso definir o center e zoom level.
A função 'zoomToMaxExtent' permite fazer com que o mapa encaixe no tamanho da janela com o maior zoom possível.
Juntando todas as partes tem-se o código HTML para vizualizar o primeiro Mapa.
<html>
<head>
<title>OpenLayers Example</title>
<script
src="http://openlayers.org/api/OpenLayers.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div style="width:100%; height:100%" id="map"></div>
<script defer="defer" type="text/javascript">
var map = new OpenLayers.Map('map');
var wms = new OpenLayers.Layer.WMS( "OpenLayers WMS",
"http://labs.metacarta.com/wms/vmap0", {layers: 'basic'} );
map.addLayer(wms);
map.zoomToMaxExtent();
</script>
</body>
</html>
Adicionar um Overlay WMS
As Layers WMS tem a capacidade de sobrepor outras Layers WMS numa mesma projecção, definindo-se para tal como um Overlay.
Isto pode ser feito de diversas maneiras. Definir o parametro transparent como true é a melhor opção no caso WMS.
Como adicionar um Overlay WMS transparente a um Map.
var twms = new OpenLayers.Layer.WMS( "World Map",
"http://world.freemap.in/cgi-bin/mapserv?",
{ map: '/www/freemap.in/world/map/factbooktrans.map',
transparent: 'true', layers: 'factbook',
format: 'png'} );
map.addLayer(twms);
--->>>> imggtngstrtd2
Google Maps
Para criar um Google Map no OpenLayers é necessário incluir uma tag script Google Maps para o dominio em questão,
especificando a respectiva chave da Google Maps API.
Example script URL for Google Maps
<script src="http://maps.google.com/maps?file=api&v=2&key=YourKey"
type="text/javascript"></script>
Uma vez incluída a esta tag, basta adicionar um novo tipo de Layer ao Map:
Creating a Hybrid Map, and adding it to the map
var google = new OpenLayers.Layer.Google( "Google", { type: G_HYBRID_MAP } );
map.addLayer(google);
Neste exemplo é utilizado um mapa do tipo G_HYBRID_MAP, o G_SATELLITE_MAP também é suportado.
--->>>> imggtngstrtd1
Exemplos, passo a passo
Neste secção, vamos demonstrar alguns exemplos de como utilizar algumas das funcionalidades do OpenLayers.
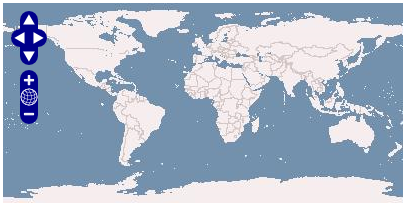
- Utilizar o OpenLayers numa página Web, é simples e fácil. Para tal, basta incluir o seguinte código na página:
<iframe
src="http://openlayers.org/viewer/"
width="400" height="200"
scrolling="no"
marginwidth="0" marginheight="0"
frameborder="0">
</iframe>
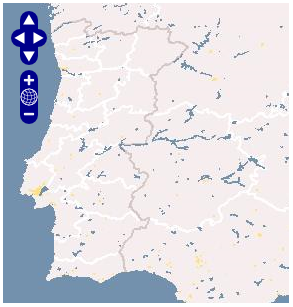
- Para especificar, por exemplo, as coordenadas de latitude e longitude e o nível de zoom, utiliza-se os parâmetros URL, Center e Zoom:
<iframe
src="http://openlayers.org/viewer/?center=39.5,-7&zoom=6"
width="100%" height="300"
scrolling="no"
marginwidth="0" marginheight="0"
frameborder="0">
</iframe>
Estes exemplos utilizam mapas, recebendo-os dinamicamente de um servidor WMS.
Guia de Utilização
http://trac.openlayers.org/wiki/UserGuide
Funcionalidades Avançadas
Exemplo de uma app já com muita cena :)
Fornecedores de Serviços
Features:
- Load map data from many sources:
Outros Recursos
http://dev.openlayers.org/apidocs/index/General.html
Before Getting Started -- The Technologies Behind OpenLayers
We at !OpenLayers generally assume that everyone who comes to us is already a highly skilled web programmer. Such, however, is not always the case. Here we have assembled a few quick links to tutorials and the like on how to master the art of coding in !JavaScript, debug in Firebug, understand JSON, etc.
* Introduction to JavaScript by the people at mootools. * Four-part video series by Douglas Crockford on Programming in JavaScript * Crockford's JavaScript page * Introduction to JSON * Debugging with Firebug
Obter o Código
Getting the Code
Releases are made available on the downloads page. Additionally, if you wish to use OpenLayers in a web application, you can include http://www.openlayers.org/api/OpenLayers.js in your page, to always get the latest release.
The code is also available in our Subversion repository. Using Subversion, you can keep up to the absolute bleeding edge of the code. If you wish to report a bug in the API, and you are able to use Subversion, please see if the bug has been fixed in Subversion first: OpenLayers is under rapid development, so things change quickly.
If you don't have Subversion or don't want to download the code, you can still try some live examples on openlayers.org. If you're familiar with JavaScript, try viewing the source of the examples to get an idea how the OpenLayers library is used.
OpenLayers is still undergoing rapid development, so expect a lot to change in the next few weeks and months. We need your support! Please check the wiki for the very latest updates and documentation, and thank you for taking an interest.